sdfsd
Vitamin B12 (As Methylcobalamin)
|
Technical Data Sheet
Net weight: 0.1kgs/Tin; Gross weight: 0.3Kgs±0.1kg/Tin 36 months under in a well-closed container and away from moisture, light, oxygen. Packed in paper-drums or carton with two plastic-bags inside. |
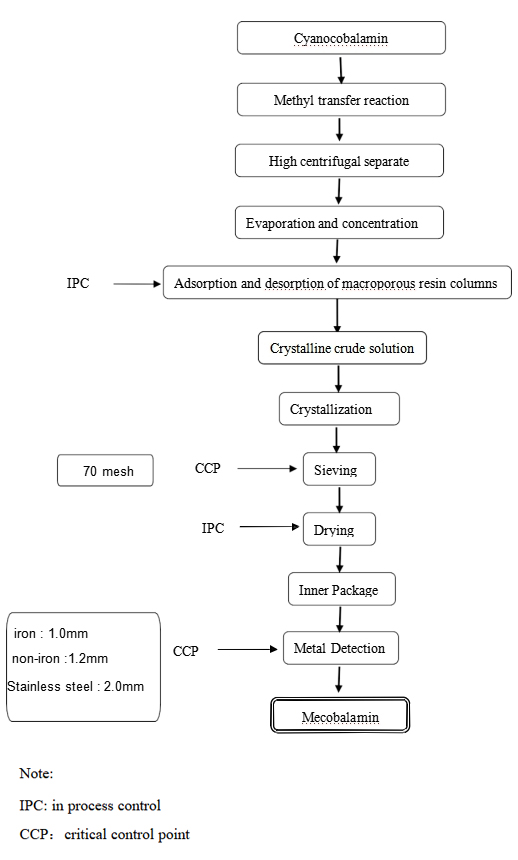
Mecobalamin FLOW CHART
|
Vitamin B12(Methylcobalamin)
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin found in foods such as meat, fish, and dairy. It can also be made in a lab and is often taken with other B vitamins.
Vitamin B12 is required for the function and development of many parts of the body, including the brain, nerves, and blood cells. Methylcobalamin is the active form of vitamin B12. Cyanocobalamin, which must be processed by the body into the active form, is the most common type used in supplements.
People commonly use vitamin B12 for vitamin B12 deficiency, cyanide poisoning, and high levels of homocysteine in the blood. It is also used for canker sores, cataracts, Alzheimer disease, osteoporosis, fatigue, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these other uses.
Uses & Effectiveness
Effective for
A rare inherited condition marked by vitamin B12 deficiency (Imerslund-Grasbeck disease). Injecting vitamin B12 as a shot for 10 days followed by monthly injections is effective for treating this condition. Vitamin B12 shots can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Vitamin B12 deficiency. Taking vitamin B12 by mouth, as a shot, or inhaling through the nose can treat and prevent vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 shots can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Likely Effective for
Cyanide poisoning. Administering hydroxocobalamin (Cyanokit), a natural form of vitamin B12, as a shot is likely effective for treating cyanide poisoning. It has been approved by the US FDA for this use. Vitamin B12 shots can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Possibly Effective for
Canker sores. Applying an ointment containing vitamin B12 or taking vitamin B12 under the tongue seems to help reduce canker sore symptoms.
High levels of homocysteine in the blood (hyperhomocysteinemia). Taking vitamin B12 by mouth, along with folic acid and sometimes pyridoxine (vitamin B6), can lower blood levels of homocysteine.
Nerve pain caused by shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Injecting vitamin B12 in the form of methylcobalamin under the skin six times weekly for up to 4 weeks reduces pain in people with nerve damage from shingles. Vitamin B12 injections can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Possibly Ineffective for
Decline in memory and thinking skills that occurs normally with age. Taking vitamin B6, folic acid, and vitamin B12 by mouth doesn't improve mental function in elderly people.
Cataracts. Taking vitamin B12 by mouth along with vitamin B6 and folic acid doesn't seem to prevent cataracts in females. It might even increase the risk of needing to have cataracts removed.
Disorders that affect when a person sleeps and when they are awake. Taking vitamin B12 by mouth does not seem to help people with sleep disorders.
Memory and thinking skills (cognitive function). Taking vitamin B12 by mouth, alone or with folic acid and vitamin B6, doesn't seem to improve memory and thinking skills in elderly people.
Fall prevention. Taking folic acid with vitamin B12 by mouth doesn't seem to prevent falls in older people also taking vitamin D.
Weak and brittle bones (osteoporosis). Taking vitamin B12 and folic acid by mouth, with or without vitamin B6, doesn't seem to reduce fractures in older people with osteoporosis.
Physical performance in elderly adults. Taking vitamin B12 and folic acid by mouth doesn't seem to help improve physical function in older people.
There is interest in using vitamin B12 for a number of other purposes, but there isn't enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
Side Effects
When taken by mouth: Vitamin B12 is likely safe for most people. Vitamin B12 is considered safe even in large doses.
When applied to the skin: Vitamin B12 is likely safe for most people when used appropriately.
When sprayed into the nose: Vitamin B12 is likely safe for most people. Vitamin B12 is considered safe even in large doses.
Special Precautions and Warnings
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Vitamin B12 is likely safe when taken by mouth during pregnancy or breast-feeding in the amounts recommended. The recommended amount for pregnancy is 2.6 mcg per day. Those breast-feeding should take 2.8 mcg per day. The safety of larger amounts is unknown.
Post-surgical stent placement: Avoid using a combination of vitamin B12, folate, and vitamin B6 after receiving a coronary stent. This combination may increase the risk of blood vessel narrowing.
Allergy or sensitivity to cobalt or cobalamin: Do not use vitamin B12 if you have this condition.
Interactions
We currently have no information for VITAMIN B12 interactions.
Dosing
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient. Fish, shellfish, meat, eggs, and dairy products are good sources of vitamin B12. The amount that should be consumed on a daily basis is called the recommended dietary allowance (RDA). The RDA is 2.4 mcg daily for people 18 years and older. While pregnant, the RDA is 2.6 mcg daily. While breastfeeding, the RDA is 2.8 mcg daily. In children, the RDA depends on age.
People over 50 years of age are advised to eat foods fortified with vitamin B12 or to take a vitamin B12 supplement. 25-100 mcg daily has been taken by mouth to maintain vitamin B12 levels in older adults. Speak with a healthcare provider to find out what dose might be best for a specific condition.
from:https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-926/vitamin-b12
CONTACT US
Add:4A-Buliding A3, 2nd Liheng Industrial Park,Fanhuan Road,Hefei 230092,China
TEL: (+86) 551 62828690
Fax: (+86) 551 62828697
Email: sales@health-sources.com
Copyright © HEALTH SOURCES NUTRITION CO., LTD.
Our website contains material and information intended for B2B customers, suppliers and distributors, and is not intended as information to the final consumers. The statements on this website have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. In developing claims for a food, beverage or supplement product label, manufactures should seek guidance to assure compliance with the appropriate regulatory authority.